|
The original text is written in Chinese and the English version is translated by Google. If in doubt, please refer to the original text.
Music electric signal and SpectrumElectric
signal A line can be divided into an infinite number of the line segments. In each segment, there are an infinite number of points Any point on the line segment and the trend of this point extending to the next point constitute an infinitesimal line segment. Any infinitesimal line segment on the track of the music electrical signal can be represented by a sine wave of a certain frequency and represents a frequency component. Technically, we use sine waves to interpret electrical music signals. This is because the sine wave has only a single frequency component on the spectrogram and can be regarded as the purest signal. In this way, we can more conveniently follow the trajectory guided by the theory of electronic technology and accept the specifications of various laws in various aspects such as equipment design and analysis. However, music information involves both the time domain and the frequency domain. The frequency and amplitude of music sounds will change over time. In music electrical signals, the appearance of a certain frequency component does not necessarily continue to the end of the entire sine wave fluctuation cycle (360 degrees). In other words, every time the frequency components appear in the music electrical signal, they are not always in the unit of the entire sine wave fluctuation period. Spectrum A time axis can be divided into infinite time periods. Each period contains an infinite number of time points.
Spectrum
in a specific period:
Instantaneous frequency spectrum: the time-frequency information spectrum cutting surface at a specific time point on the time axis, which represents the instantaneous frequency spectrum of a music time-frequency information at that time point. At any point on the time axis, where there is always a corresponding instantaneous frequency spectrum of music time-frequency information. Created by Chen Last revision date: Aug-2019
All rights reserved by Chen Audio Laboratory, Inc. |
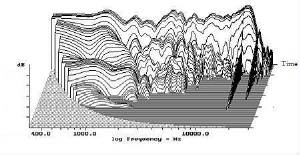 Time-frequency information spectrum:
Time-frequency information spectrum: